FAC STRATEGIC REVIEW
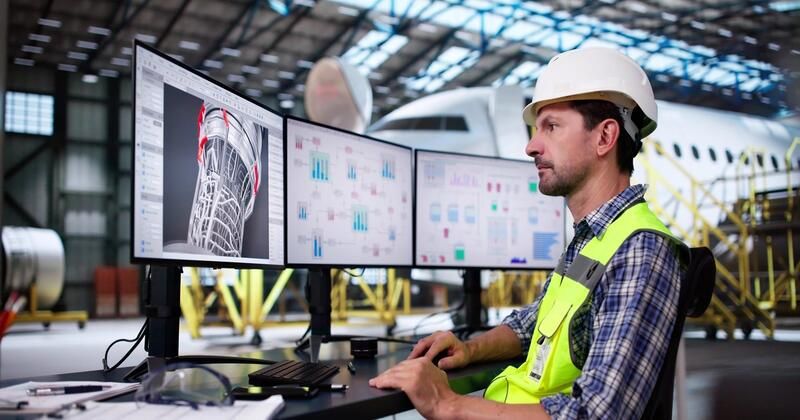

AI is revolutionizing aerospace advanced manufacturing by enhancing design, quality, efficiency, and predictive capabilities—driving safer, smarter, and more scalable production.
Here are the top five impacts of AI on the aerospace manufacturing sector.
1. Enhanced Quality Control and Inspection
- AI-powered computer vision systems detect microscopic defects in components with greater speed and accuracy than manual inspection.
- Reduces rework, scrap rates, and costly recalls by ensuring parts meet stringent aerospace standards.
2. Generative Design and Engineering Optimization
- AI algorithms analyze design parameters to generate lightweight, high-strength structures that meet performance goals.
- Enables faster prototyping and innovation, with companies like Boeing using AI to reduce component weight and improve aerodynamics.
3. Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Monitoring
- Machine learning models analyze sensor data to forecast equipment failures before they occur.
- Minimizes downtime, extends asset life, and improves safety by enabling proactive maintenance strategies.
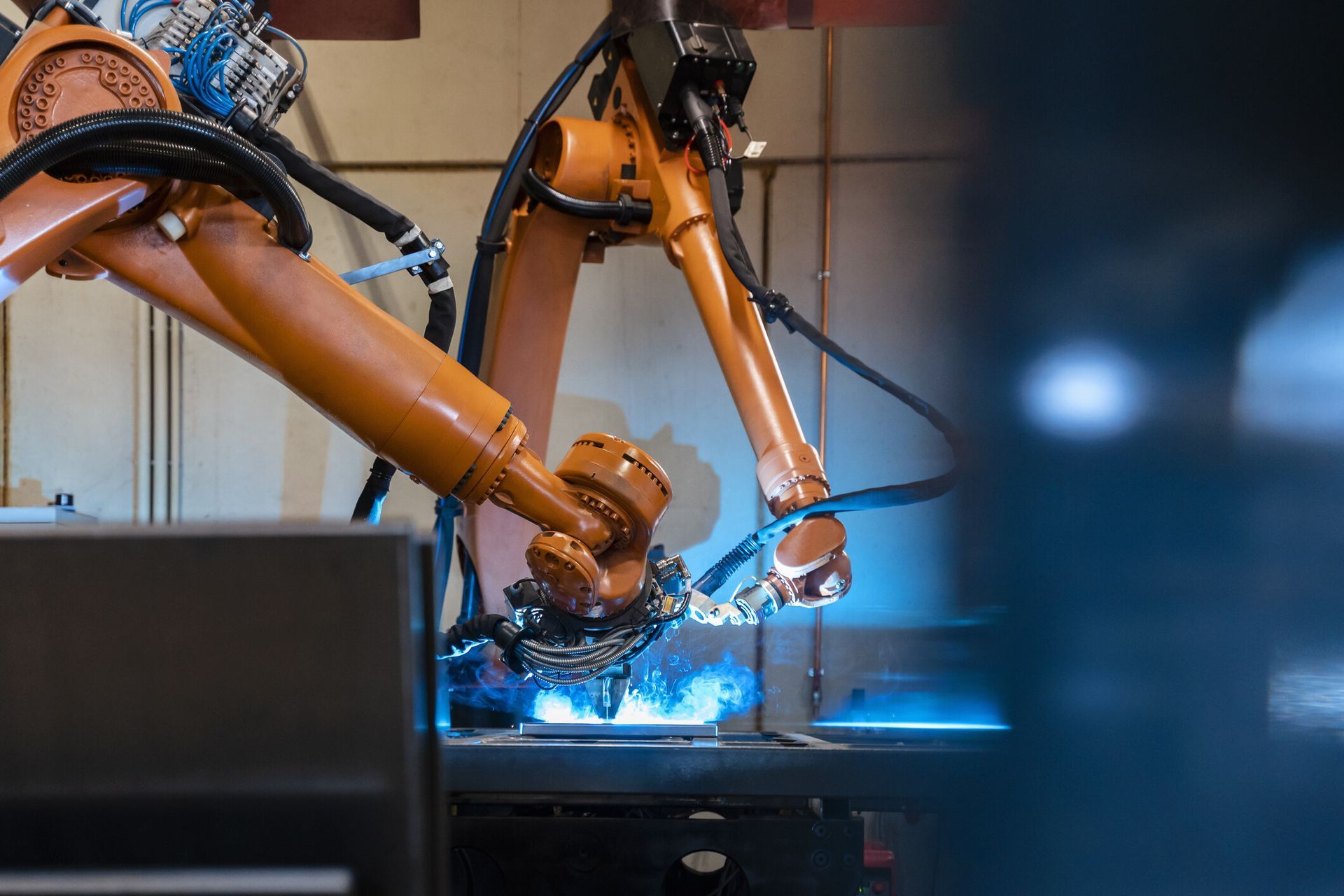
4. Autonomous Manufacturing and Robotics
- AI-driven robots perform complex tasks such as welding, assembly, and inspection with adaptive learning and precision.
- Boosts throughput, reduces human error, and supports scalable production in high-mix, low-volume environments.
5. Supply Chain and Inventory Optimization
- AI predicts material shortages, manages inventory levels, and streamlines procurement.
- Enhances responsiveness to demand fluctuations and reduces waste across the aerospace supply chain.
These impacts are reshaping how aerospace manufacturers design, build, and maintain aircraft and components—ushering in a new era of intelligent, data-driven production.
From a business perspective the shift to AI adoption is an imperative, not just to stay competitive, but to fundamentally transform how they operate, innovate, and grow. Here’s why:
1. Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
- AI automates repetitive tasks, optimizes production schedules, and reduces waste.
- Predictive analytics minimize downtime and maintenance costs by identifying issues before they escalate.
- McKinsey reports up to 20–30% cost savings in manufacturing operations through AI-driven optimization.
2. Quality Assurance and Compliance
- AI-powered vision systems detect defects with greater accuracy than human inspectors.
- Real-time monitoring ensures adherence to industry standards (e.g., ISO, AS9100), reducing rework and recalls.
- This is especially critical in sectors like aerospace and medical devices, where precision is non-negotiable.
3. Faster Innovation Cycles
- Generative design tools use AI to explore thousands of design permutations, accelerating R&D.
- AI simulations reduce the need for physical prototyping, shortening time-to-market.
- Companies like Airbus and GE use AI to design lighter, stronger components with fewer iterations.
4. Supply Chain Resilience
- AI forecasts demand, identifies supplier risks, and optimizes inventory levels.
- It enables manufacturers to respond quickly to disruptions, geopolitical shifts, or material shortages.
- Gartner estimates that AI-enabled supply chains are 50% more responsive to volatility.
5. Workforce Augmentation and Safety
- AI supports human workers with intelligent assistance, reducing cognitive load and improving decision-making.
- Cobots (collaborative robots) adapt to human workflows, enhancing safety and productivity.
- Training simulations powered by AI improve onboarding and upskilling in complex environments.
6. Strategic Advantage and Scalability
- AI enables manufacturers to scale operations without proportionally increasing headcount or infrastructure.
- It supports data-driven decision-making across finance, HR, and operations.
- Early adopters gain a strategic edge in bidding, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
In short, AI isn’t just a tool—it’s a catalyst for smarter, leaner, and more resilient manufacturing.
Aerospace firms in South East England can begin adopting AI by focusing on strategic planning, workforce development, and targeted pilot programs aligned with operational goals.
Here’s a structured roadmap tailored to aerospace manufacturers in the region:
1. Assess Readiness and Identify Use Cases
- Conduct an AI maturity audit: Evaluate current digital infrastructure, data availability, and process automation levels.
- Prioritize high-impact areas: Focus on quality control, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization—areas where AI delivers immediate ROI.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve engineering, operations, and IT teams to align AI goals with business strategy.
According to the ONS, firms with strong management practices are significantly more likely to adopt AI successfully.
2. Build Strategic Partnerships
- Collaborate with local universities and innovation hubs: Institutions like the University of Southampton and Cranfield University offer aerospace and AI expertise.
- Join regional clusters: Engage with South East Aerospace Alliance or Innovate UK networks to access funding, case studies, and peer support.
- Leverage government programs: Tap into DSIT’s AI sector initiatives and grants for digital transformation.
These partnerships reduce risk and accelerate learning curves.
3. Invest in Workforce Upskilling
- Train staff in AI fundamentals and data literacy: Use modular courses or apprenticeships focused on AI in manufacturing.
- Create cross-functional AI teams: Blend domain experts with data scientists to ensure practical, scalable solutions.
- Promote a culture of experimentation: Encourage small-scale pilots and iterative learning.
ONS data shows that lack of internal expertise is a major barrier to AI adoption.
4. Start with Pilot Projects
- Choose low-risk, high-value pilots: Examples include defect detection using computer vision or predictive maintenance on CNC machines.
- Use cloud-based platforms: Avoid heavy infrastructure costs by leveraging SaaS tools with built-in AI capabilities.
- Measure outcomes: Track KPIs like downtime reduction, inspection accuracy, and throughput improvements.
The WMCA roadmap recommends phased implementation with clear metrics to guide scaling.
5. Ensure Data Governance and Compliance
- Establish secure data pipelines: Ensure data integrity and cybersecurity, especially for sensitive aerospace IP.
- Align with industry standards: Comply with AS9100, ISO 27001, and emerging AI safety regulations.
- Document AI decisions: Maintain audit trails for transparency and regulatory readiness.
This builds trust and ensures long-term viability of AI systems.
By following this roadmap, aerospace firms in South East England can transition from exploratory interest to operational AI deployment—unlocking efficiencies, improving quality, and strengthening competitiveness.



